Unlocking the Benefits of Hydronic Design
Hydronic design is a system that utilizes water to transfer heat in a building, offering numerous benefits in terms of energy efficiency, comfort, and versatility. By understanding the basics of hydronic design and its key components, one can appreciate the advantages it brings to different settings. Furthermore, with the continuous technological advancements and its role in green building, hydronic design is undoubtedly the future of heating systems. However, it is essential to overcome the challenges related to installation, maintenance, and cost considerations. This article will delve into these aspects, unlocking the benefits and potential of hydronic design.
Understanding the Basics of Hydronic Design
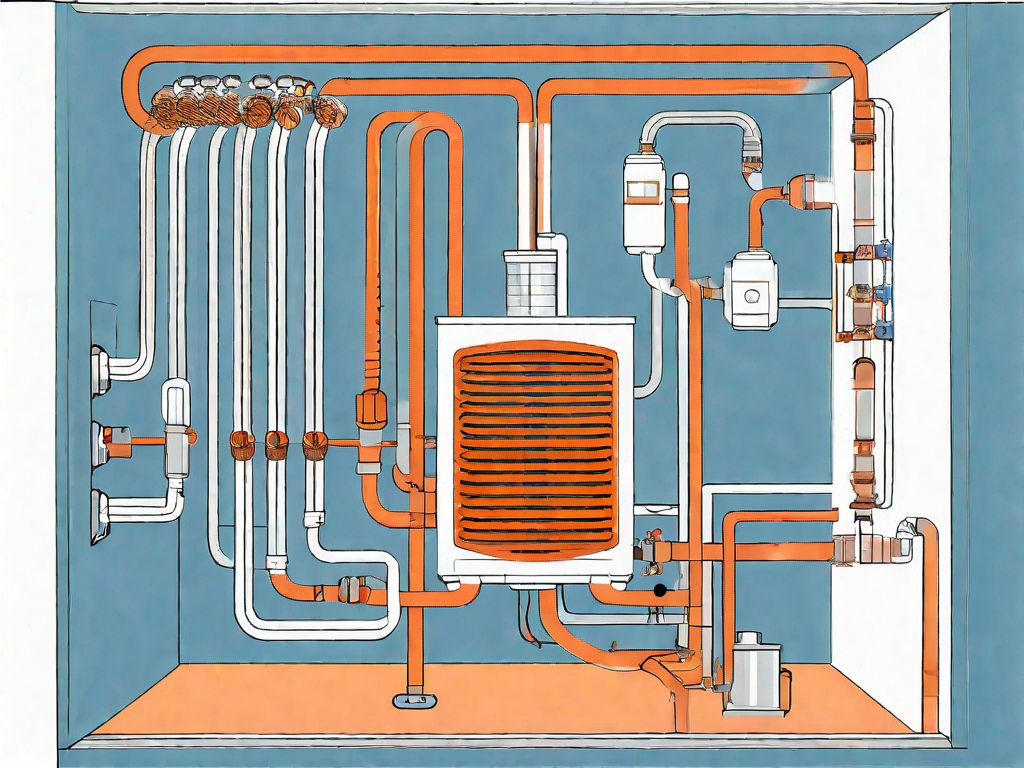
Hydronic design is founded on the principle that water can efficiently transfer heat. The system consists of a boiler, circulator pumps, piping, and heat emitters such as radiators or underfloor heating. The hot water is produced by the boiler and circulated throughout the building, providing warmth.
In hydronic design, the pump is responsible for the movement of water, avoiding the need for forced airflow common in traditional heating systems. This circulation ensures a consistent distribution of heat, eliminating cold spots and drafts.
The Principle Behind Hydronic Systems
The principle behind hydronic systems lies in the ability of water to absorb and release heat efficiently. Water has a higher specific heat capacity than air, meaning it can store more heat energy per unit of mass. This property allows hydronic systems to provide longer-lasting warmth, even after the boiler stops operating.
Furthermore, the water in a hydronic system can also act as a thermal mass, absorbing excess heat during periods of high demand and releasing it gradually when the demand decreases. This thermal inertia helps to stabilize the indoor temperature, reducing temperature fluctuations and providing a more comfortable environment.
Key Components of a Hydronic System
A typical hydronic system comprises several key components. The boiler heats the water, which is then pumped through the piping network by circulator pumps. Heat emitters, such as radiators or underfloor heating, release the heat into the room, warming the space effectively. Thermostats and control valves are used to regulate the temperature, ensuring comfort and energy efficiency.
Moreover, hydronic systems often incorporate zone control, allowing different areas of a building to be heated independently. This zoning capability enables users to customize the temperature settings in different rooms or zones, optimizing comfort and energy usage.
Additionally, expansion tanks are included to accommodate the expansion of water as it heats up, preventing pressure buildup within the system. These tanks act as a safety measure, ensuring the system operates within its designed parameters and avoiding any potential damage or failures.
Furthermore, hydronic systems can be integrated with renewable energy sources, such as solar thermal collectors or geothermal heat pumps. By harnessing these sustainable technologies, hydronic design can further enhance energy efficiency and reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
By incorporating these essential components and design principles, hydronic systems offer numerous advantages over traditional heating methods. They provide efficient, comfortable, and customizable heating solutions that can adapt to various building types and user preferences.
The Advantages of Hydronic Design
Hydronic design offers various advantages compared to traditional heating systems, making it a popular choice in residential, commercial, and industrial settings.
When it comes to energy efficiency and sustainability, hydronic design truly shines. By utilizing water as the heat transfer medium, hydronic systems can achieve high levels of efficiency. Water's high specific heat capacity allows it to store and release heat more effectively, reducing energy consumption. This efficiency not only leads to significant cost savings but also contributes to a more sustainable approach to heating. By choosing hydronic design, you are not only benefiting your wallet but also the environment.
But it's not just about energy efficiency; hydronic design also ensures a comfortable and consistent heating experience. Unlike forced-air systems, which can create temperature variations and drafts, hydronic systems distribute heat evenly throughout the space. This even heat distribution eliminates cold spots and maintains a comfortable temperature throughout the building. Imagine walking into a room and feeling the warmth embrace you, without any uncomfortable drafts or temperature fluctuations. That's the kind of comfort that hydronic design provides.
Furthermore, hydronic design offers flexibility and versatility. It can accommodate various heat emitters, including radiators, underfloor heating, or even fan coil units. This versatility allows hydronic systems to adapt to different architectural designs and satisfy individual preferences. Whether you prefer the classic elegance of radiators or the seamless warmth of underfloor heating, hydronic design can cater to your needs. It seamlessly integrates into any space, providing both functionality and aesthetic appeal.
Additionally, hydronic design is known for its durability and longevity. The closed-loop system ensures that the water remains free from contaminants, preventing corrosion and extending the lifespan of the system. With proper maintenance, a hydronic system can last for decades, providing reliable and efficient heating for years to come.
In conclusion, hydronic design offers a multitude of advantages that make it a preferred choice in heating systems. From energy efficiency and sustainability to comfort, flexibility, and longevity, hydronic design ticks all the boxes. So, if you're looking for a heating solution that not only keeps you warm but also saves you money and reduces your environmental impact, hydronic design is the way to go.
Implementing Hydronic Design in Different Settings
Hydronic design is a versatile heating solution that can be implemented in various settings, catering to diverse heating needs. Whether it's a residential home or a commercial/industrial building, hydronic design offers optimal heating comfort and energy efficiency.
Residential Applications
In residential settings, hydronic design provides an excellent heating solution that ensures both comfort and efficiency. It can be used for space heating as well as domestic hot water supply. One of the popular applications of hydronic design in residential homes is in-floor radiant heating systems.
In-floor radiant heating systems offer luxurious warmth and comfort, making it a preferred choice for homeowners. These systems eliminate the need for visible radiators or baseboard heaters, enhancing the interior aesthetics of the living space. Imagine stepping onto a warm floor on a chilly winter morning, it's a delightful experience that hydronic design can provide.
Moreover, hydronic design in residential applications offers precise temperature control, allowing homeowners to adjust the heating according to their preferences. This level of control ensures a comfortable living environment throughout the year.
Commercial and Industrial Applications
Hydronic design finds extensive use in commercial and industrial buildings, where large spaces need to be efficiently heated. These settings often require heating solutions that can handle high demand and provide consistent warmth.
One of the key advantages of hydronic design in commercial and industrial applications is its ability to offer precise temperature control. This ensures comfortable working conditions for employees, which can have a positive impact on productivity and overall well-being.
Additionally, hydronic systems can be integrated with other energy sources, such as solar water heaters, to further enhance sustainability. By harnessing the power of the sun, these systems can reduce energy consumption and lower operating costs.
Furthermore, hydronic design in commercial and industrial settings allows for zoning, which means different areas can be heated to different temperatures based on their specific requirements. This zoning capability ensures efficient energy usage and reduces unnecessary heating in unoccupied areas.
In conclusion, hydronic design is a versatile heating solution that can be implemented in both residential and commercial/industrial settings. It offers optimal heating comfort, energy efficiency, and precise temperature control. Whether it's a cozy home or a large industrial facility, hydronic design can provide the warmth and comfort needed for a comfortable living or working environment.
The Future of Hydronic Design
The future of hydronic design is bright, with continuous advancements and its integral role in green building practices.
Technological Advancements and Innovations
Ongoing technological advancements are driving the evolution of hydronic design. Smart thermostats and automation systems allow for increased control and optimization of heating, further improving energy efficiency. Integration with renewable energy sources, such as heat pumps, opens up possibilities for even greener heating solutions.
The Role of Hydronic Design in Green Building
As green building practices become more prevalent, hydronic design plays a vital role in achieving energy-efficient and sustainable heating systems. It aligns with the goals of reducing carbon emissions, minimizing energy consumption, and utilizing renewable energy sources. Hydronic design offers an effective solution for heating without compromising environmental responsibility.
Overcoming Challenges in Hydronic Design
While hydronic design brings numerous benefits, several challenges need to be addressed for successful implementation.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
The installation of a hydronic system requires careful planning and expertise. Proper sizing and design of the piping system are essential to ensure efficient heat distribution. Regular maintenance, including proper water treatment and inspection of components, is crucial for the longevity and optimal performance of the system.
Cost and Budgeting Factors
Hydronic design may involve higher upfront costs compared to traditional heating systems. However, the long-term energy savings and increased comfort justify the investment. Proper budgeting and understanding the overall cost-effectiveness are vital considerations when implementing hydronic design.
In conclusion, hydronic design unlocks a range of benefits for heating systems. Its efficient heat transfer, energy savings, and comfort make it an excellent choice for various settings. The continuous advancements in technology and its role in sustainable construction further strengthen its position as the future of heating. By addressing installation challenges and considering cost factors, hydronic design can provide reliable, efficient, and environmentally responsible heating solutions for many years to come.