The Basics of HVAC Design
In any building, HVAC systems play a crucial role in providing comfort and maintaining a healthy indoor environment. Understanding the basics of HVAC design is essential for architects, engineers, and building owners. This article provides an overview of HVAC systems, their components, how they work, and the importance of proper design in terms of energy efficiency and indoor air quality.
Understanding HVAC Systems
HVAC stands for heating, ventilation, and air conditioning. These systems control the temperature, humidity, and air quality to create a comfortable environment inside a building. HVAC systems can be centralized or decentralized, depending on the size and purpose of the building.
To grasp the fundamentals of HVAC design, it is important to understand the key components that make up these systems.
When it comes to HVAC systems, there are several components that work together to achieve the desired indoor conditions. These components are crucial in ensuring that the system operates effectively and efficiently. Let's take a closer look at each of these components:
Components of HVAC Systems
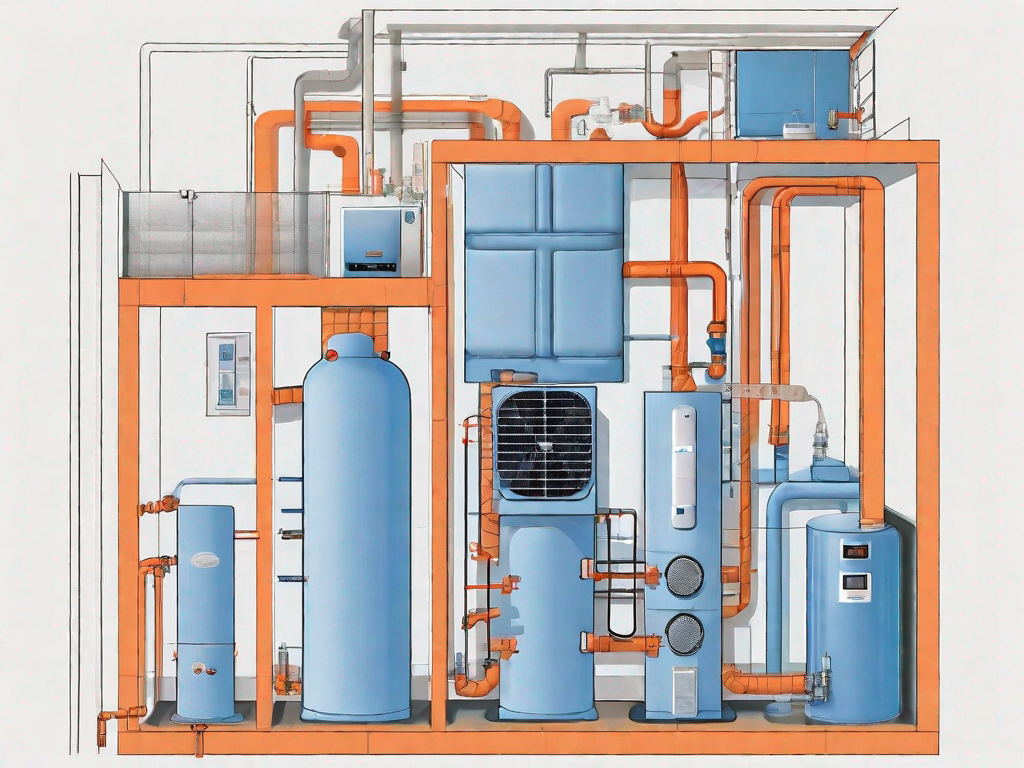
HVAC systems consist of several components that work together to achieve the desired indoor conditions. The major components include:
1. Heating Equipment: Furnaces, boilers, or heat pumps are used to provide warmth during cold weather. These heating equipment extract heat from a fuel source, such as gas or electricity, and transfer it to the indoor air. This process raises the indoor temperature, ensuring a comfortable environment for occupants. 2. Cooling Equipment: Air conditioners, chillers, or heat pumps are used to cool the indoor air during hot weather. These cooling equipment extract heat from the indoor air and transfer it outside, effectively lowering the indoor temperature. This process is essential in maintaining a pleasant and cool environment inside the building. 3. Ventilation Equipment: Fans, blowers, and ductwork are used to distribute fresh air throughout the building and remove stale air. Ventilation equipment plays a crucial role in maintaining indoor air quality by introducing outdoor air and removing pollutants, odors, and excess moisture. This ensures a healthy and comfortable environment for occupants. 4. Air Distribution System: Ductwork carries conditioned air to different areas of the building, ensuring uniform distribution. The air distribution system plays a vital role in delivering the conditioned air to various spaces in the building, providing thermal comfort to occupants. Properly designed ductwork helps in maintaining consistent temperature and air quality throughout the building. 5. Controls: Thermostats, sensors, and control systems regulate the operation of HVAC equipment to maintain desired conditions. These controls monitor temperature, humidity, and other parameters, and adjust the operation of the HVAC system accordingly. This ensures optimal performance and energy efficiency of the system. 6. Air Filtration: Filters remove dust, allergens, and pollutants from the air to enhance indoor air quality. Air filtration is an important component of HVAC systems as it helps in removing harmful particles from the air, ensuring a healthy and clean environment for occupants. Regular maintenance and replacement of filters are essential to ensure their effectiveness.
Each component plays a vital role in the overall performance of an HVAC system. The proper design, installation, and maintenance of these components are crucial in ensuring the efficiency and effectiveness of the system.
How HVAC Systems Work
Understanding the basic operation of HVAC systems is important for designing effective and efficient systems. HVAC systems operate on the principles of heat transfer and thermodynamics.
During the heating mode, the heating equipment extracts heat from a fuel source (such as gas or electricity) and transfers it to the indoor air. The conditioned air is then distributed throughout the building to raise the indoor temperature. This process ensures that occupants are kept warm and comfortable during cold weather.
On the other hand, during the cooling mode, the cooling equipment extracts heat from the indoor air and transfers it outside. This process removes heat from the building, lowering the indoor temperature and creating a cool and comfortable environment for occupants during hot weather.
The ventilation equipment ensures a constant supply of fresh air by introducing outdoor air and removing stale air. This process helps in maintaining indoor air quality by diluting pollutants, odors, and excess moisture. The air distribution system delivers the conditioned air to various spaces in the building, providing thermal comfort to occupants.
By understanding how HVAC systems work, designers and engineers can create systems that are tailored to meet the specific needs of a building, ensuring optimal performance and energy efficiency.
Importance of HVAC Design
Proper HVAC design is vital as it directly impacts both energy efficiency and indoor air quality. A well-designed system ensures optimal performance, minimizes energy consumption, and enhances occupant comfort.
When it comes to HVAC design, there are several key factors that need to be considered. These factors not only contribute to the overall efficiency of the system but also play a significant role in maintaining a healthy indoor environment.
Role in Energy Efficiency
An efficiently designed HVAC system can significantly reduce energy consumption and operating costs. By considering factors such as building orientation, insulation, and heat recovery systems, designers can reduce heat gain or loss and optimize energy performance.
For example, proper building orientation can maximize natural light and reduce the need for artificial lighting, resulting in lower energy usage. Insulation, on the other hand, helps to minimize heat transfer between the interior and exterior of the building, reducing the load on the HVAC system.
In addition to these factors, the selection of energy-efficient equipment and the implementation of advanced control strategies can further enhance the overall energy efficiency of the system. For instance, variable speed drives and smart thermostats can adjust the system's operation based on the actual demand, ensuring that energy is not wasted.
Proper HVAC design can contribute to sustainable building practices and help meet energy efficiency goals. By reducing energy consumption, it not only benefits the environment but also leads to significant cost savings for building owners and occupants.
Impact on Indoor Air Quality
HVAC systems play a critical role in maintaining indoor air quality. Proper ventilation ensures an adequate supply of fresh air, diluting indoor pollutants and minimizing the risk of airborne contaminants.
Efficient air filtration systems are another crucial aspect of HVAC design. These systems capture dust, allergens, and airborne particles, improving the overall air quality. By removing these contaminants, the HVAC system helps create a healthier indoor environment, particularly for individuals with respiratory conditions or allergies.
Moreover, a well-designed HVAC system prevents the growth and spread of mold. Mold can thrive in damp and poorly ventilated spaces, leading to respiratory issues and allergies. By considering factors such as air distribution, filtration, and humidity control, HVAC designers can create a healthy and comfortable indoor environment.
It's worth noting that proper maintenance and regular cleaning of HVAC systems are equally important in ensuring optimal indoor air quality. Filters should be replaced or cleaned regularly, and air ducts should be inspected and cleaned to prevent the accumulation of dust and other contaminants.
In conclusion, HVAC design goes beyond simply providing heating, ventilation, and air conditioning. It plays a crucial role in energy efficiency and indoor air quality. By considering various factors and implementing the right strategies, HVAC designers can create systems that not only save energy but also provide a comfortable and healthy indoor environment for occupants.
Principles of HVAC Design
When designing an HVAC system, several principles must be considered to ensure optimal performance and comfort.
Load Calculations
Load calculations are necessary to determine the heating and cooling requirements of a building. By considering factors such as the building's location, insulation, occupancy, and heat gain/loss, designers can accurately size the HVAC equipment. Proper load calculations prevent oversizing or undersizing, ensuring efficient operation.
System Selection and Sizing
Based on load calculations, designers can select the appropriate HVAC equipment, such as furnaces, boilers, air conditioners, or heat pumps. Proper sizing of the equipment is crucial to meet the heating and cooling demands of the building. Undersized equipment may result in insufficient comfort, while oversizing can lead to excessive energy consumption and higher costs.
HVAC Design Process
The HVAC design process typically involves several stages, starting from initial planning and assessment to detailed design and specification.
Initial Planning and Assessment
During the planning stage, designers assess the building's size, purpose, and layout. They consider factors such as occupancy, insulation, orientation, and local climate conditions. This information helps in determining the appropriate HVAC system type and capacity.
Detailed Design and Specification
Once the initial planning is complete, designers proceed with the detailed design and specification. They select the specific HVAC equipment, design the air distribution system, and specify controls and sensors. Detailed documentation, including drawings and specifications, is prepared to guide the installation and commissioning process.
Common HVAC Design Mistakes
Although HVAC design is a complex process, certain common mistakes should be avoided to ensure optimal system performance and occupant comfort.
Oversizing or Undersizing Systems
Misjudging the load calculations can result in oversized or undersized HVAC systems. Oversized systems tend to short-cycle, leading to inefficient operation and increased wear and tear. Undersized systems may struggle to meet the desired indoor conditions, causing discomfort. Proper load calculations and equipment selection are crucial to avoid these issues.
Ignoring Ductwork Design
Ductwork design is often overlooked, leading to airflow issues and temperature imbalances. Improperly designed ducts can result in restricted airflow, noise, and inefficient operation. Proper duct sizing, routing, and insulation are essential for effective HVAC system performance.
In conclusion, understanding the basics of HVAC design is crucial for creating comfortable and energy-efficient indoor environments. By considering factors such as load calculations, system selection, and following a systematic design process, HVAC designers can ensure optimum performance and occupant satisfaction. Avoiding common design mistakes, such as oversizing or undersizing systems and neglecting ductwork design, is essential to achieve long-term success. Proper HVAC design contributes to efficient energy consumption, improved indoor air quality, and overall occupant well-being.